The bond bears have been in ascendance this week, even before the release of the latest minutes from the last Federal Open Market Committee meeting. The yield on the 10-year Treasury has jumped 23.7 basis points this week, the largest four-day yield gain since June 5, 2020, as the Fed minutes showed discussion of a fast winddown of its balance sheet alongside rising interest rates.
Granted, this was a discussion from Dec. 14 and 15, though St. Louis Fed President James Bullard’s comments on Thursday suggested the more aggressive stance outlined in the minutes was still very much current thinking.
David Rosenberg, chief economist and strategist at Rosenberg Research and the former chief North American economist at Merrill Lynch, isn’t buying the tough talk from the Fed. “One should be skeptical of the Fed’s forecasts, given the poor track record, even though investors treat them (and the dot plots and FOMC minutes) as gospel,” he says.
Dating back to 2012, the Fed’s forecasts on rates have been correct 37% of the time, accurate on core inflation 29% of the time, accurate on unemployment 24% of the time and accurate on real gross domestic product growth 17% of the time. And the Fed tends to be too bullish on growth, he adds.
“What I’m saying is that they say in the stock market never to bet against the Fed but in the bond market, I can definitely tell you that it is perfectly safe to say that you can bet against the Fed’s forecasting ability — especially when it comes to the one thing the Fed can actually control, which is the policy rate,” he says. Pointing to flattening real consumer spending, housing past its peak, too much inventory, a record high trade deficit and flat-to-down real business speaking, “there is absolutely no impetus to domestic demand growth going forward and yet the Fed continues to play the role of economic cheerleader.”
If the Fed were to hike to 1.75% next year, it would mean the possibility of a 20% decline in home values and a 30% slide in equity prices, if there were a mean reversion in price-to-income ratios. Even now, both asset classes are overpriced by 15%, he says.
He recommends in the stock market shying away from cyclical sensitivity and toward defensive growth such as healthcare, staples and utilities; and in corporate credit, trading up in quality.
The chart
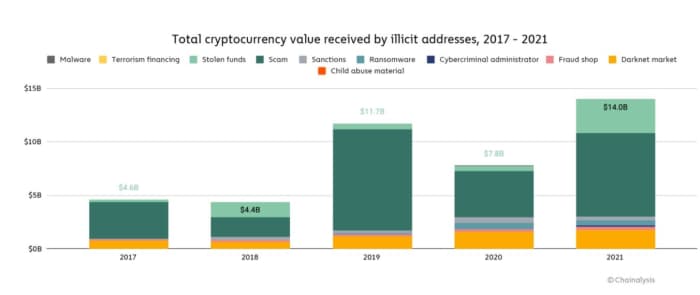
Cryptocurrency crime reached a record $14 billion last year, according to research company Chainalysis, with scammers taking $7.8 billion and outright theft of $3.2 billion. As a percent of all transactions, however, the company said crypto crime was at a record low, since total volumes jumped 567% but illicit activity rose by 79%.