(Bloomberg) — The Federal Reserve will unveil details of what policy makers debated last month that may shed light on how they view the near-term path for interest rates amid surging inflation and signs of a slowing economy.
Chair Jerome Powell has said the Fed could hike by either 50 basis points or 75 basis points in July. He made the remarks at a June 15 press conference after policy makers raised rates by 75 basis points in the largest hike since 1994. The Fed will publish minutes of the meeting at 2 p.m. in Washington on Wednesday.
Several policy makers since the June decision have said they are open to going big again at their meeting later this month to curb the hottest price pressures in 40 years. They include Fed Governors Michelle Bowman and Christopher Waller, as well as regional Fed presidents Loretta Mester, Mary Daly and Charles Evans.
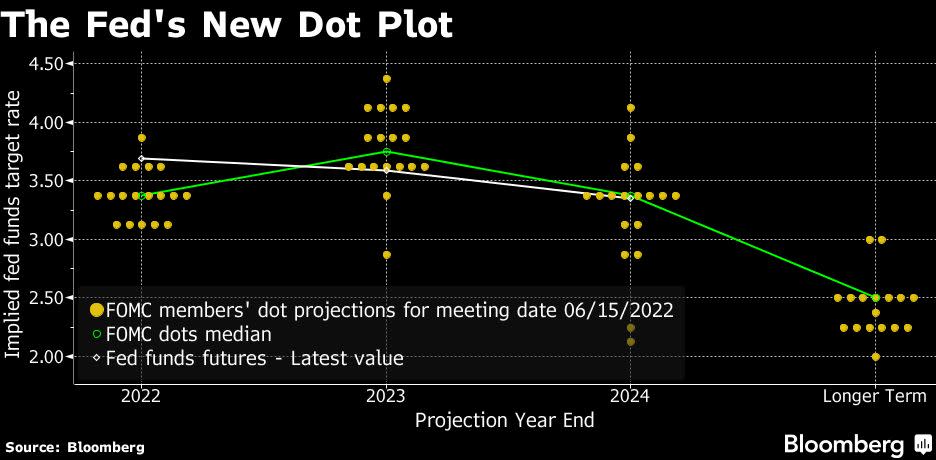
Updated quarterly projections of the 18 policy makers show the median participant on the Federal Open Market Committee sees rates rising to 3.4% at year’s end and 3.8% next year, from a current target range of 1.5% to 1.75%.
“We will be looking for clues about the indicators that the committee will be weighing in its upcoming July meeting as it deliberates whether to hike 50 basis points or 75 basis points,” said Jonathan Millar, economist with Barclays Plc. The minutes might reinforce the idea “that the FOMC is prioritizing price stability over attaining a soft landing,” he said.
The committee’s view of inflation expectations may well be a lengthy topic of discussion.
What Bloomberg Economics Says…
“We expect the discussion in the minutes to indicate that policy makers were worried about the un-anchoring of inflation expectations. There may be multiple references of how high gasoline and food prices could affect households’ inflation psychology, justifying the Fed’s shift in placing more focus on headline inflation measures rather than just core measures as they usually do.”
— Anna Wong, chief US economist
Inflation
In his press conference following the Fed’s last meeting, Powell cited the preliminary University of Michigan survey of inflation expectations as among the factors prompting policy markets to raise rates by 75 basis points in a late shift. The initial reading showed Americans expecting 3.3% inflation over the next five to 10 years, but that was revised down to 3.1% in the final report released June 24.
“Are they putting more weight on consumer expectations — which are mostly impacted by food and energy prices — or are they worried about professional forecasters and markets, which suggest they have the issue under control?” said Drew Matus, chief market strategist with MetLife Investment Management. “It seems they are more focused on the consumer, but that is dangerous given how inflation expectations are driven.”
While Powell has said now is not the time for “nuanced readings” on inflation, any discussion of the underlying dynamics of prices could be important, given the growing divergence between the Fed’s preferred measure of inflation, based on personal consumption, and the consumer price index, said Luke Tilley, Wilmington Trust’s chief economist.
The minutes could also provide insights into how the FOMC would view a decline in economic activity. A number of Wall Street economists have lowered their forecasts for second-quarter growth, and the Atlanta Fed’s popular tracking estimate currently shows a contraction for the quarter, even as the labor market has stayed strong.
Slowing Growth
While Powell has declared that the battle against high inflation is “unconditional,” the committee could have a range of views on whether it would be necessary to adjust plans in light of any softer data.
“The most important thing will be any discussion around what might cause the Fed to deviate from the projected path,” said Stephen Stanley, economist at Amherst Pierpont Securities. “Powell has very much emphasized the inflation-fighting part of the job. The growth versus inflation aspects of monetary policy come into tension if the economy does slow down.”
The odds of a US recession in the next year are 38% in the next 12 months, according to the latest forecast of Bloomberg Economics, after consumer sentiment hit a record low and interest rates surged.
While FOMC participants are not identified by name, the minutes could also give insight into whether others on the committee shared the concerns of Kansas City Fed chief Esther George, whose dissent from the 75 basis-point hike surprised Wall Street. George in previous years has been a hawk and only dissented in favor of tighter policy.
In a statement on June 17, George said the size of the move, combined with the shrinking of the central bank’s balance sheet, created uncertainty about the outlook.
©2022 Bloomberg L.P.