(Bloomberg) — The Federal Reserve’s interest-rate hikes are wearing out their welcome in bond markets, with a measure of the yield curve that Chair Jerome Powell has highlighted as a recession indicator sending out a warning message.
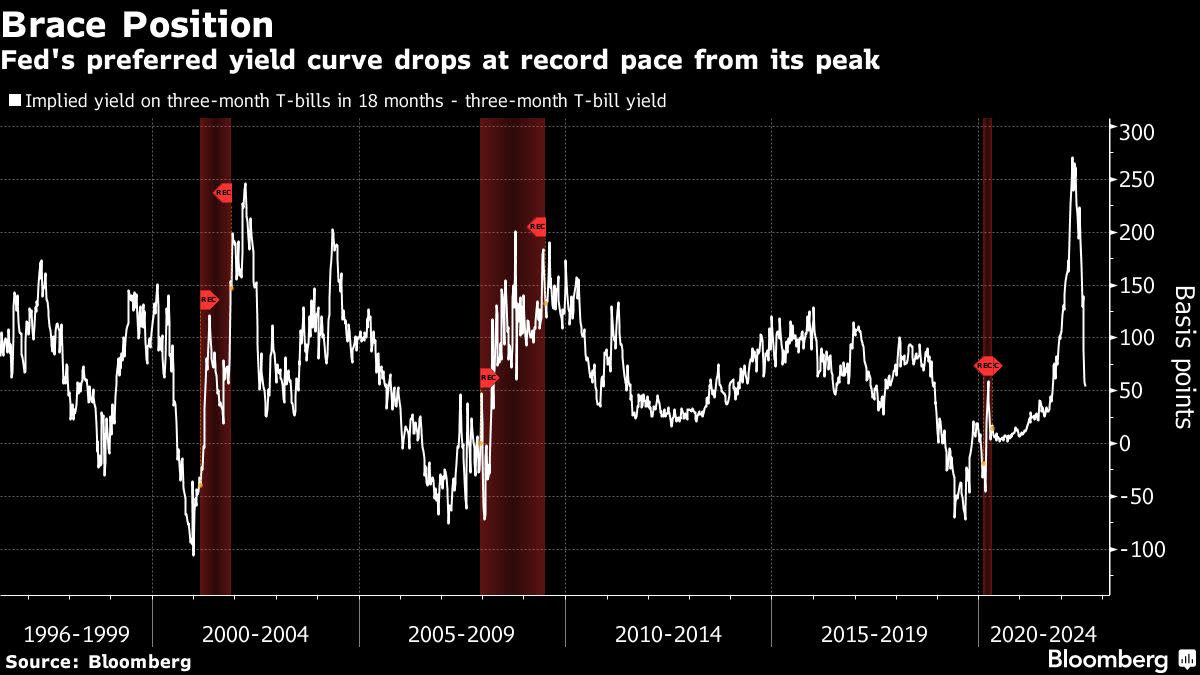
The difference between rates on where three-month bills are now and where they will be in 18 months has tumbled about 95 basis points in July, the biggest monthly decline in data starting in 1996. A vast swathe of the US yield curve inverted in recent weeks as recession fears spurred investors to pile into longer maturities.
The conundrum for the Fed is that readings on inflation drivers — such as wages — are elevated enough to sustain pressure on policy makers to stay hawkish, even as measures of the broader economy such as last week’s business-activity data signal the US is heading for a severe economic slowdown.
“Rates markets pricing in 2023 Fed rate cuts imply the market is expecting the Fed to pivot on rising recession risks,” said Prashant Newnaha, a strategist at TD Securities in Singapore. However, with official inflation data yet to confirm a peak, the Fed is likely to maintain its war on inflation despite signs the US and European economies are slowing, and this should see curves flatten further, he said.
Yields on US two-year notes have climbed above those on five-year securities by the most since 2007, while the two-to-10-year curve is most the most inverted since 2000 at around minus 24 basis points. Powell downplayed such inversions back in March by arguing the three-month to 18-month forward curve was the one that really mattered, and it was steepening.
That spread peaked soon after his comments, and is now dropping fast enough to fall below zero at some stage in the next month.
While US gross domestic product data due Thursday may show the world’s biggest economy has already entered a recession, bond investors could be about to discover that that data point alone won’t be enough to quiet Fed hawks, according to TD Securities’ Newnaha. The company is forecasting GDP to have contracted by 1% in the second quarter, he said.
©2022 Bloomberg L.P.