(Bloomberg) — The globe is in the grips of a climate crisis as temperatures soar and rivers run dry, and yet it’s never been a better time to make money by digging up coal.
The energy-market shockwaves from Russia’s invasion of Ukraine mean the world is only getting more dependent on the most-polluting fuel. And as demand expands and prices surge to all-time highs, that means blockbuster profits for the biggest coal producers.
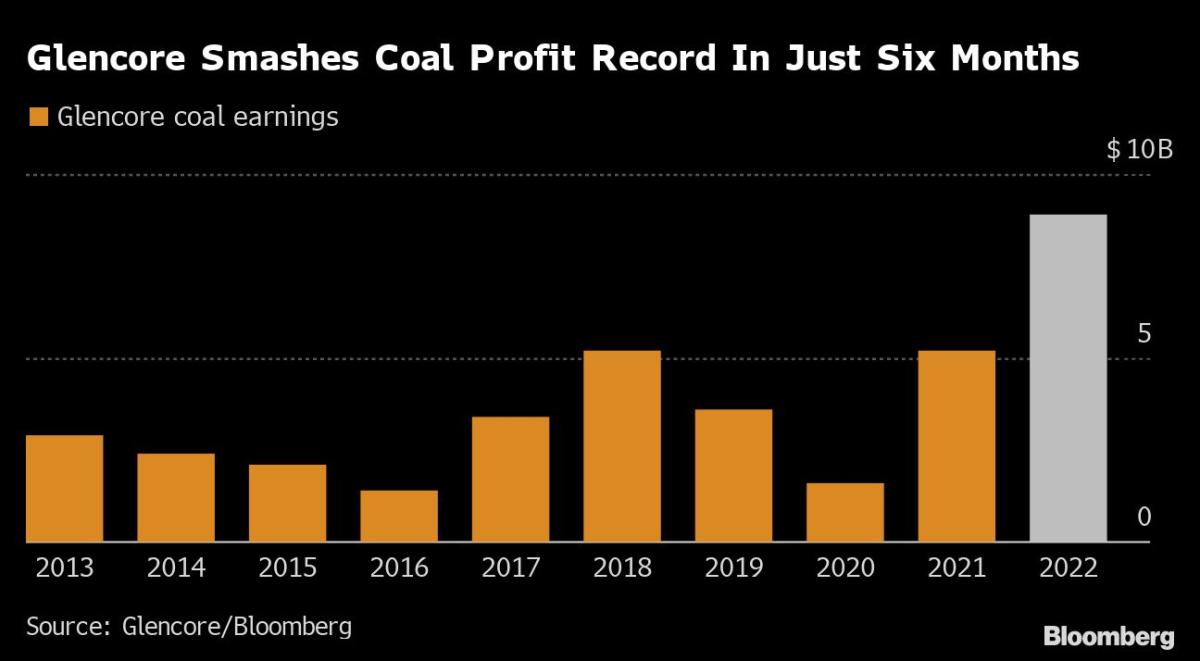
Commodities giant Glencore Plc reported core earnings from its coal unit surged almost 900% to $8.9 billion in the first half — more than Starbucks Corp. or Nike Inc. made in an entire year. No. 1 producer Coal India Ltd.’s profit nearly tripled, also to a record, while the Chinese companies that produce more than half the world’s coal saw first-half earnings more than double to a combined $80 billion.
The massive profits are yielding big pay days for investors. But they will make it even harder for the world to kick the habit of burning coal for fuel, as producers work to squeeze out extra tons and boost investment in new mines. If more coal is mined and burned, that would make the likelihood of keeping global warming to less than 1.5 degrees Celsius even more remote.
It’s a remarkable turnaround for an industry that spent years mired in an existential crisis as the world tries to shift to cleaner fuels to slow global warming. Banks have been pledging to end financing, companies divested mines and power plants, and last November world leaders came close to a deal to eventually end its use.
Ironically, those efforts have helped fuel coal producers’ success, as a lack of investment has constrained supply. And demand is higher than ever as Europe tries to wean itself off Russian imports by importing more seaborne coal and liquefied natural gas, leaving less fuel for other nations to fight over. Prices at Australia’s Newcastle port, the Asian benchmark, surged to a record in July.
The impact on profits for the coal miners has been stunning and investors are now cashing in. Glencore’s bumper earnings allowed the company to increase returns to shareholders by another $4.5 billion this year, with the promise of more to come.
Gautam Adani, Asia’s richest person, capitalized on a rush in India to secure import cargoes amid a squeeze on local supply. Revenue generated by his Adani Enterprises Ltd. jumped more than 200% in the three months to June 30, propelled by higher coal prices.
US producers are also reaping bumper profits, and the biggest miners Arch Resources Inc. and Peabody Energy Corp. say demand is so strong at European power plants that some customers are buying the high-quality fuel typically used to make steel to generate electricity instead.
The wild profits threaten to become a political lightning rod as a handful of coal companies cash in while consumers pay the price. Electricity costs in Europe are at record highs and people in developing nations are suffering daily blackouts because their utilities can’t afford to import fuel. Earlier this month, United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres lashed out at energy companies, saying their profits were immoral and calling for windfall taxes.
Coal’s advocates say the fuel remains the best way to provide cheap and reliable baseload power, especially in developing countries. Despite the huge renewable rollout, burning coal remains the world’s favorite way to make power, accounting for 35% of all electricity.
While western producers cash in on the record prices — with companies such as Glencore committed to running mines to closure over the next 30 years — top coal consumers India and China still have growth on the agenda.
The Chinese government has tasked its industry with boosting production capacity by 300 million tons this year, and the nation’s top state-owned producer said it would boost development investment by more than half on the back of record profits.
Coal India is also likely to pour a large chunk of its earnings back into developing new mines, under government pressure to do more to keep pace with demand from power plants and heavy industry.
China and India worked together at a UN conference in Glasgow last year to water down language in a global climate statement to call for a “phase down” of coal use instead of a “phase out.”
At the time, few would have predicted just how expensive the fuel would become. Just a year ago, the biggest international mining companies — excluding Glencore — were in a full retreat from coal, deciding the paltry returns were not worth the increasing pressure from investors and climate activists.
When Anglo American Plc spun off its coal business and handed it over to existing shareholders, one short seller, Boatman Capital, said the new business was worth nothing. Instead the stock — known as Thungela Resources Ltd. — skyrocketed, gaining more than 1,000% since its June 2021 listing, with first-half earnings per share up about 20-fold.
Glencore itself snapped up a Colombian mine from former partners Anglo and BHP Group. The nature of the deal, and rising coal prices, meant Glencore essentially got the mine for free by the end of last year. In the first six months of this year, it made $2 billion in profit from that one mine, more than double its entire coal businesses earnings in the same period last year.
The earnings look set to keep rolling in, as analysts and coal executives say the market will remain tight.
“As we stand today, we don’t see this energy crisis going going away for some time,” Glencore Chief Executive Officer Gary Nagle said.
©2022 Bloomberg L.P.