(Bloomberg) — Commodities have opened the fourth quarter in some style, with prices posting the biggest weekly gain since March after OPEC+ agreed to chop oil supply. The coming week will bring a host of signals on the outlook over the rest of the year and into 2023 before earnings season hits full flood.
In energy, highlights include outlooks from the International Energy Agency and Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries as investors gauge prospects for demand, Europe’s energy crisis, and the impact of sanctions on Russia flows. In crop markets, the US Department of Agriculture lifts the veil on its vital WASDE snapshot. In addition, minutes from the Federal Reserve’s September rate-setting meeting, due Wednesday, and US inflation data on Thursday, will shape the debate on interest rates, which may swing gold prices.
Here are some of the main items for investors to track next week, with attention also falling on struggles along the Mississippi River as water levels dwindle; China’s return to the fray after a week-long break; and key data from Asia on the world’s most-consumed cooking oil. Rounding it off is some seriously expensive gasoline, with California prices on the cusp of a record.
Tackling the Uncertainty Principle
The oil market is currently so stacked with uncertainty that even Saudi Arabia’s energy minister said this week that he’s never known a situation like it, weighing in after presiding over an OPEC+ supply cut drove a surge in prices. As such, traders will be looking to influential monthly reports next week from the International Energy Agency and the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries for much-needed clues about the shape of things to come. The IEA’s analysis comes on Thursday, one day after the cartel issues its take.
The biggest worry on the demand side is the outlook for global growth as central banks tighten policy, hurting energy consumption. On the supply side, the market will be looking for any numbers on how big the hit to Russian supply could be when EU sanctions on flows come into force in December. After the OPEC+ salvo, Goldman Sachs Group Inc. and Morgan Stanley both painted bullish outlooks into year-end suggesting prices may regain $100 a barrel.
Grains of Information
As concerns swirl over farm exports getting out of Ukraine and a global recession crimping grain demand, the US Department of Agriculture releases its latest crop estimates Wednesday. The agency stunned markets at the end of September with reports showing smaller-than-expected US wheat and corn supplies, together with bigger-than-forecast soybean stockpiles.
Those findings will be folded into the October report known as WASDE. While drought has squeezed US corn output, it’s still not clear by exactly how much. The dryness depleting Mississippi River water levels is driving up barge freight rates, making American corn extra expensive. The costly crop and limited supply could prompt USDA to trim US export projections. Analysts, on average, expect USDA to cut its estimate for US corn yields. Any reduction in yields or crop sizes will cause volatility as stockpiles are still tight.
Mississippi Blues
In a crisis reminiscent of the problems that struck Europe’s mighty Rhine River earlier this year, waterborne trade along the Mississippi River is suffering as drought cuts flows. The vital US waterway ferries key commodities between the heart of America and the Gulf Coast, and water levels are already so low in some spots that barges are getting stuck, causing vessel traffic to get backed up. With little relief in sight, the situation may worsen over the coming week.
Major barge lines have been turning away spot business as they struggle to meet demand for grains, metals and other raw materials already contracted well in advance. It’s a worrisome development for transporting goods from a river basin that produces 92% of the nation’s agricultural exports, especially during harvest season. The river is a main artery for crop exports, while petroleum, fertilizer and imported steel also transit parts of the waterway.
Palm Reading
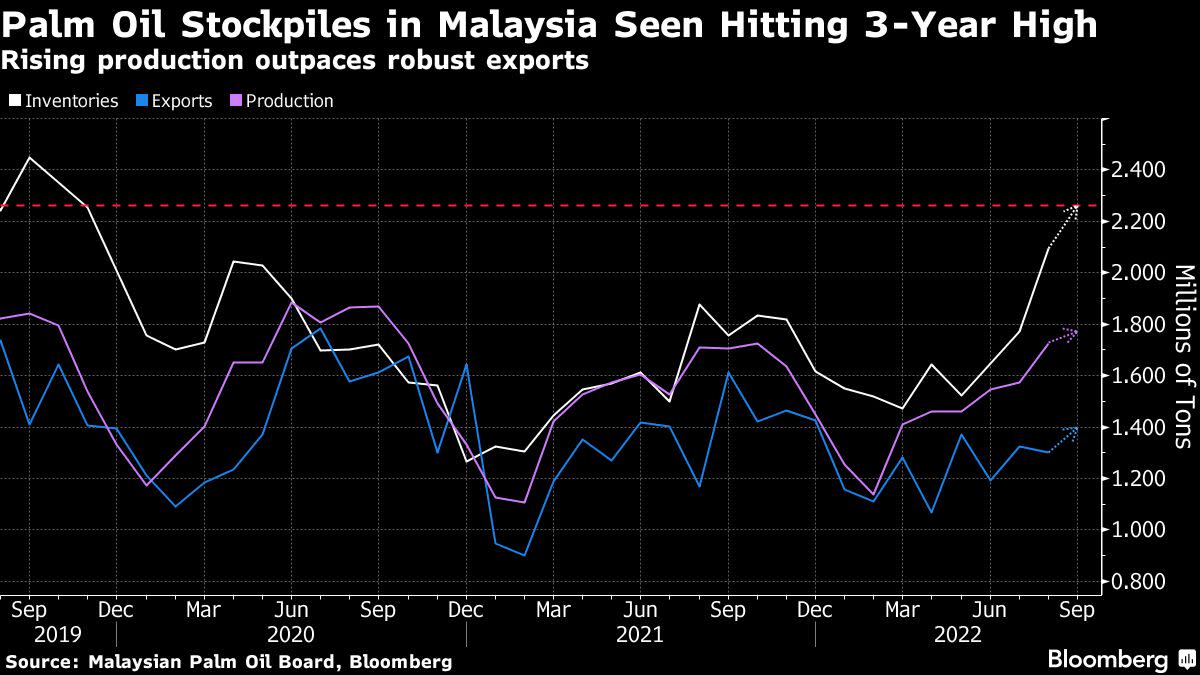
The surging cost of cooking oils helped drive global food inflation to a record in March but now, at long last, relief is at hand. The canola crop in Canada has rebounded, and the soybean crop now being planted in Brazil, the biggest grower, is expected to jump to an all-time high. Next week traders look to Asia, with palm oil stockpiles in No. 2 grower Malaysia seen hitting the highest in almost three years, industry estimates show. Figures come on Tuesday.
The revival is just as well because the outlook for sunflower oil supply from war-torn Ukraine remains dire. Farmers have harvested only 20% of the area sown to sunflowers, half of last year’s figure, because of the Russian invasion. There’s also concern that the Kremlin may tighten conditions for Ukraine’s export corridor in the Black Sea when it comes up for renewal next month.
China on My Mind
Markets in commodity powerhouse China reopen on Monday after a week-long break as investors prepare for the pivotal Communist Party congress. Ahead of the event, which is set to start on Oct. 16, there’ll be a couple of pointers on the state of Asia’s largest economy and what that means for raw materials demand. On Tuesday, the IMF publishes its World Economic Outlook, which may spotlight the slowdown in the nation’s growth, costs that come with Beijing’s Covid-Zero policy, property-market woes, and, possibly, options for stimulus.
While banks have been busy pruning their GDP forecasts, Premier Li Keqiang said recently that China’s economy had stabilized in the third quarter and the final three months of the year would be key to the nation’s recovery. Additional insight will come on Friday with the first batch of trade data for September, including figures for flows of everything from iron ore to soybeans.
Pump Action
Californian drivers are on edge as fuel prices at the pump are once again flirting with record highs. Retail prices are close to hitting a new all-time high for the second time this year. The average price at the pumps is threatening to top the mid-June record $6.438 a gallon, according to data from auto club AAA.
Gasoline prices typically fall after the summer travel season but tight supplies on the West Coast are keeping costs elevated. Stockpiles are at the lowest in a decade. California tends to lean toward higher prices, with the state separated by the Rocky Mountains from the energy hubs of the Gulf Coast and Midwest.
©2022 Bloomberg L.P.